We all are pretty well aware of increasing environmental issues like water and air pollution and global warming. Sadly, it is the human’s ever-growing demand for resources which is putting tremendous pressure on the biodiversity of our natural world.
Coming to the construction industry, this industry is responsible for producing the largest amount of greenhouse gases and destruction waste. Buildings also consume a huge amount of energy during its construction phase and even more during its operations phase. Despite the fact, that services like lighting, water heating, air conditioning, provide ease of living to the building dwellers, these services consume a massive amount of energy and add to the increasing pollution levels. Added to that are the denizen activities which produce enormous amounts of solid and water wastes.
Green Buildings are truly the need of the hour in India. If the country’s architects, builders, designers and the Indian Green Building Council (IGBC) have their way, most of the buildings in India (old and new) will soon turn environment-friendly, decreasing the amount of power they gobble.
Currently, India has over 400 crore sq ft of registered green footprint, i.e. the second largest globally. By 2022, Indian Green Building Council (IGBC) is aiming 1000 crore sq ft of sustainable footprint. Now you may ask who is Indian Green Building Council (IGBC), let us discuss their story and why is there so much buzz around them.
What Are Green Buildings?
For the past few years, the word ‘Green Buildings’ is endlessly hogging limelight in the media. But, what exactly are these structures? How are they different from other buildings? And why are they green?
In simplest terms, a green building is the one that uses less water, energy and other natural resources, creates lesser amount of waste and greenhouse gas emissions, and are healthy for its occupants as compared to the regular building structures. Building a Green Structure is about constructing buildings which enhance the use of local materials, local ecology and most significantly they are built to cut power, water, and material requirements.
Green Building Rating Systems
So, Who Decides A Green Building Is Really Green? Whether a Green building is really green is to be decided against predefined rating systems. In India, Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment (GRIHA), Indian Green Building Council (IGBC), and Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) are the three primary Rating systems.
The main purpose of any green building rating system is to guarantee that an existing or upcoming construction project incorporates the finest green building practices which would ensure constant savings and higher operation and processes.
Indian Green Building Council (IGBC)
Indian Green Building Council was formed in the year 2001 as a part of the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII). The vision of the IGBC is, “To enable a sustainable built environment for all and facilitate India to be one of the global leaders in the sustainable built environment by 2025”.
The council offers an extensive array of services which include:
- Developing new green building rating programmes
- Certification services
- Green building training programmes
Green Building Congress which is IGBCs annual flagship event on green buildings is also organised by this council. IGBC is committee-based, member-driven and consensus-focused. All the participants of the construction industry including of developers, architects, product manufacturers, Government, corporate, academia and nodal agencies actively participate in the council activities through local chapters.
IGBC closely works with numerous State and Central Governments, World Green Building Council (WGBC), bilateral multi-lateral agencies in endorsing green building notions in the country.
Green Building Movement In India
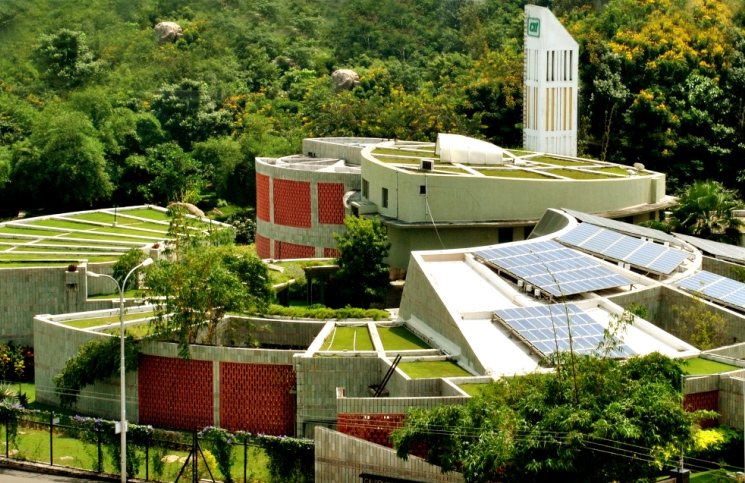
The Green Building movement in India gained momentum in 2003 when CII-Sohrabji Godrej Green Business Centre building in Hyderabad was bestowed with the first and the most respected Platinum-rated green building rating in India. From just about 20,000 sq.ft in 2003 to 450 crores sq.ft green footprint in India today IGBC is playing a catalytic role in leading the green building movement in India.
As on 16th April 2018, more than 4,553 Green Buildings developments coming up with a footprint of over 5.29 Billion sq.ft are itemized with IGBC, out of these 1336 Green Building projects are certified and copiously functional.
Today almost all kinds of building structures are choosing to go Green – Government, Offices, Residential, Institutions, IT Parks, Banks, Convention Centre, Airports, Institutions, Hotels, Hospitals, Factories, Townships, Metros, Schools, etc.
IGBC Green Ratings
The main goal of any green building rating system is to make sure that any existing or imminent construction project incorporates optimum green building practices which would ensure sustained savings and higher operations. Indian Green Building Council Green ratings are all-inclusive, user-friendly and strong and also offer the best services to its stakeholders.
These rating systems are based on the five elements of nature (panchabhutas) and are a blend of ancient architectural practices and modern state-of-the-art technological innovations. Most prominently, they address the national priorities like:
- Conservation of natural resources
- Sustainable Infrastructure
- Water efficiency
- Energy efficiency
- Handling of domestic waste
- Occupant health and well-being
- Innovation & Development
Based on these principals, CII’s Indian Green Building Council launched around 20 Green Ratings to suit different types of construction projects, let us know them:
1. IGBC Green New Buildings
This Green rating system was launched to address national priorities. It is a tool that empowers the designer to apply green concepts and decrease environmental impacts which are practically measurable. The rating programme covers methods to cover various climatic zones and changing lifestyles.
Green New buildings can have incredible advantages, both tangible and intangible. Saving in water and energy consumption right from the beginning are the most tangible ones; enhanced air quality, outstanding daylighting, health & well-being of the inhabitants, safety benefits and conservation of scarce national resources are the intangible benefits of this rating system.
2. IGBC Green Existing Buildings
This is a voluntarily and consensus-based program that is primarily focused on the sustained performance of building structures with reference to the green features. The predominant objective of this rating system is to simplify the process of implementing green strategies for the building owners and facility managers, further measure their effects and withstand the performance in the long-run.
The rating system is essentially designed to address national primacies of resource preservation at the same time providing quality of life for the occupants. Energy and water savings, enhanced air quality and health and higher satisfaction level of the occupants are among few of the benefits of Green Existing Buildings.
3. IGBC Green Homes
The Green Homes Rating System addresses the most significant national priorities that include
handling of household waste, water conservation, lessen the use of fossil fuels, energy efficiency,
lesser dependence on the usage of virgin materials and health and well-being of inhabitants.
IGBC Green Homes is one of the first rating programme developed in India, solely for the residential sector. This rating system is a measurement system designed for rating new residential buildings that include the below construction categories:
- Individual homes
- High rise residential apartments,
- Gated communities
- Row houses
Green Homes is designed mainly for new residential structures. But, it is also applicable for existing buildings designed in accord with the IGBC Green Homes standards.
4. IGBC Green Schools
Green School rating system is a totally unique system which addresses eco-education, Health and hygiene factors in addition to the infrastructural facilities, water conservation, waste management and energy efficiency. Nutrition, physical activity, and safety are other aspects which are also addressed. Few of the benefits of this rating are:
- Intensification of student’s performance through the improved indoor environment by accommodating more fresh air and natural light.
- Improve student’s health and well-being and also the overall ambiance of school.
- Advance building performance through efficient water and energy savings.
- Educate the students on green features and also sensitize the students to environmental aspects.
- Aids children to learn and take responsibility for their own actions which concern the environment.
Green Schools rating is designed in such a way that both existing schools and new schools can use the guidelines.
5. IGBC Green Affordable Housing
The Green Affordable Housing Rating system is the first-of-its-kind rating system that addresses sustainability and promotes higher living standards for the residents across all levels of society. Green ideas and techniques in the affordable housing sector can help address the below:
- Reduced consumption of energy and water.
- Better health and hygiene
- Improved sanitation
- Improved ventilation and light
- Fuel savings in transit
- Reduced pollution
This rating system is applicable for housing projects designed with carpet-area less than or equal to 60 square meters per dwelling unit, which constitute at least 70 % of the total project built-up area throughout the country.
6. IGBC Green Residential Societies
Green Residential Societies rating system under IGBC addresses green features under categories like facility management, sustainable water practices, energy conservation, waste management and innovative building practices. It is designed to address the specific requirements of existing Multi-Dwelling residential buildings.
The validity of IGBC Green Residential Societies certification is for 3 years from the date of issue. For recertification, the projects are required to show compliance with the latest version of IGBC Green Residential Societies rating dominant at the time of recertification.
7. IGBC Green Factory Buildings
Green Factories under IGBC rating system is the first of its kind that addresses sustainability in industrial buildings. The programme is primarily designed to address national primacies and quality of life for the factory workmen. Green Factory uses well-accepted national standards, also wherever local or national standards are missing, suitable international benchmarks have been considered.
This rating system addresses both new and existing factory buildings, also note it would only address the factory building structures, not the processes. It is applicable to all sectors of the industries and for climatic zones in the country.
8. IGBC Green Interiors
Indoor air, aesthetics, and comfort are of supreme importance to occupants as 90 percent of the time people stay indoors. Green Interiors under IGBC Rating system addresses green features under categories like eco-design approach, energy efficiency, indoor environment, interior materials and innovation in interior design.
This rating programme is designed to address the explicit requirements of tenants-occupied commercial spaces and can also be applied to owner-occupied spaces. Ideally, this rating suited to office interior fit-outs but can be applied to retail spaces, malls, hotels, resorts, restaurants, IT spaces, banks and other buildings.
9. IGBC Green Townships
Green Townships Rating System under IGBC is a tool which enables the designers to apply green ideas and criteria’s, in an attempt to reduce environmental impacts which are measurable. The rating system is typically designed to address large developments and makes it is mandatory to include residential development as part of the township.
Some typical examples of large-scale developments are integrated townships, satellite cities, gated communities, campuses with multiple buildings etc. Also, note this rating system is not applicable for independent buildings and land parcels.
10. IGBC Green Cities
This rating system aims to enable the development authorities and developers to apply green notions and planning principles, in an attempt to lessen negative environmental impacts which are measurable and enhance the overall quality of life. Few benefits of IGBC Green Cities are:
- Efficient Land Use
- Efficient Mobility
- Efficient City Infrastructure
- Enhanced Quality Of Life
Projects should meet certain criteria to qualify for IGBC Green Cities Rating:
- Any upcoming large-scale Development with a minimum area of 250 Ha and a minimum gross population density of 125 persons per hectare (pph).
- The city shall generate both direct and indirect employment opportunities for at least 20% of the total population
- The city should have social infrastructure facilities like, education facilities, socio-cultural facilities, sports facilities, healthcare facilities and recreational facilities
Green Cities is first of its kind rating system in the country that addresses environmental sustainability in the emerging cities.
11. IGBC Green Campus
Green concepts are now penetrating into other forms of environments like the IT Parks, Administrative campuses, Educational campuses, Healthcare campuses, Convention centers, Hospitality campuses, Industrial parks, Military campuses, Leisure & Recreational campuses, Religious campuses, etc. IGBC Green Campus rating system is designed for both New and Existing Campuses.
The green concepts and techniques in campuses aim to address National problems like water and energy efficiency, reduction in the use of fossil fuels, handling of consumer waste and conserving natural resources. Most prominently, these concepts can improve the inhabitant’s health, happiness, and well-being.
12. IGBC Green Villages
Green Village rating is structured to address rural challenges. IGBC Green Village rating is a tool for identification & implementation of green features in a village. This rating system aims to address the below mentioned national priorities:
- Clean Village and Improved Lifestyle
- Improved Drinking water and Sanitation facilities
- Adequate infrastructure for Education & Healthcare
- Reduced Potable water demand
- Effective Solid waste management
- Ensure Power security through Clean Energy
- Local Economic Development
- Digital Village Initiative
Green ideas and techniques in the villages can help in addressing National worries like water and energy availability, reduction in fossil fuel use, handling of waste and conserving natural resources. Most notably, these concepts can augment health and well-being in villages.
13. IGBC Green Healthcare Facilities
Green Healthcare Facilities Rating System under IGBC is designed for Sub-centre, Primary Health Centre, Clinics, Private Hospitals, Community Health Centre, District Hospital, and Medical Institutions.
14. IGBC Health and Well-being
The main objective of this rating is to enable the buildings to incorporate people-centric measures for advancing the health & well-being.
15. IGBC Green Data Center
The Green Data center rating system is planned to enable construction and operation of data centers with enhanced resource efficiency, thereby leading to National benefits. This rating system is designed for both new and existing data centers.
16. IGBC Green Landscapes
The prime objective of IGBC Green Landscape Rating System is to smoothen the creation of comfortable and environmentally friendly landscape for people. This rating system is comprehensive and user-friendly.
17. IGBC Green SEZs
IGBC Green SEZ facilitates the conception of energy efficient, water efficient, healthy, comfortable and environmentally friendly SEZ. It is an extension of the Green SEZ guidelines.
18. IGBC Green Mass Rapid Transit System (MRTS)
IGBC Green MRTS rating system is a tool that enables new Rail based MRTS to apply green concepts during design and construction, which helps in reducing environmental impacts which are measurable. The principal objective of IGBC Green MRTS is to ensure environmental sustainability and at the same time enhance the commuters experience.
19. IGBC Green Existing Mass Rapid Transit System (MRTS)
IGBC Green Existing MRTS rating system is a tool can enable operational Rail based MRTS to apply green ideas and sustain performance of the system with respect to the green elements during operation, so as to further reduce environmental impacts which are measurable. The main objective of this rating is to facilitate the MRTS operators in implementing green strategies, measure their impacts and endure the performance in the long run, and at the same time enhance the commuters comfort and experience.
20. IGBC Green Railway Stations
This is another first of its kind holistic rating in the country that addresses environmental sustainability in the railway stations of India. The core objective of this rating is to facilitate implementation of green ideas, in that way it reduces the adverse environmental effects due to station operation and maintenance and improve the overall commuter experience at the station.
This rating system would also help the station management understand their existing position with respect to the ‘green performance’ and the measures which need to be taken to boost the performance constantly.
Most of these rating systems are based on the Panchabhutas (the 5 elements of nature) (panchabhutas) and are a mixture of ancient architectural practices and modern state-of-the-art technological innovations. Most prominently, these aim at addressing national priorities like conservation of natural resources, water efficiency, energy efficiency, management of domestic waste and inhabitant health and well-being.
The IGBC Green Building Certification Process
IGBC green building certification procedure adopts an all-inclusive multi-pronged approach in the overall rating process:
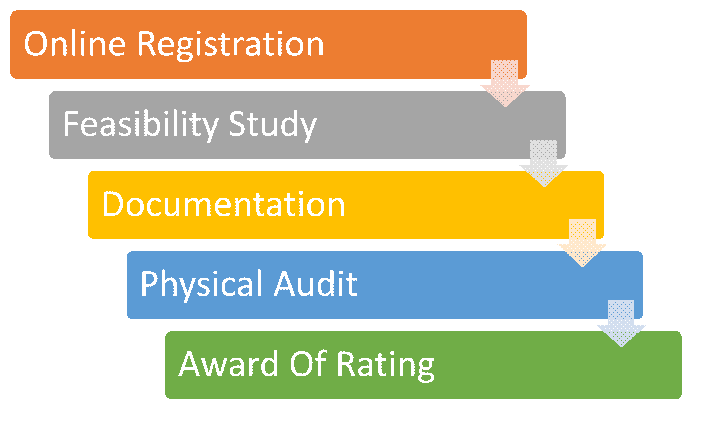
-
Online Project Registration
Project teams who are interested in IGBC Certifications for their project are required to first register with IGBC. Registration is the opening step to establish contact with IGBC and offers access to the essential documents, templates, important communications and other required information.
To register a project online one can visit the IGBC Registration Page.
Once the project is registered, the project team can begin to prepare for documentation and calculations to adhere to the mandatory requirements and credit submittal requirements.
-
Feasibility Study
Conducting a project feasibility study is one of the major steps in the process of getting an IGBC Green Certification. This empowers the project team to draw out a roadmap for attaining the desired green building rating level. The broad areas which are evaluated during this study are:
- Site Selection and Planning
- Sustainable Architecture and Design
- Site Selection and Planning
- Building Materials and Resources
- Site Selection and Planning
- Indoor Environmental Quality
- Innovation and Development
Post feasibility study comes in project facilitation, here a green building consultant plays a pivotal role. IGBC commends that project teams should consider IGBC Accredited green building consultants (IGBC APs) for the overall feasibility study and facilitation process. IGBC APs are reliable professionals who counsel the project team on various eco-friendly ideas, technologies, and products specific to the project.
-
Pre-Certification
IGBC offers developer-based projects to opt for precertification at the design stage, the outcome of which is optimization of costs and as well as resources. Pre-certification also aids in ruling out which credits and pre-requisites are more likely to be attained during the final rating. Adding further to the benefits is that it allows the developers to flaunt the proposed green features to their potential buyers or tenants.
-
Documentation
Documentation is one of the most critical steps in achieving the desired green building rating. Owing to its importance, IGBC allows project documents to be submitted in two stages.
- Preliminary Submission – This phase includes the mandatory requirements and the number of credits a project team aims for. The documents are reviewed by a third-party accessor appointed by IGBC. Further, IGBC provides review comments to the owner/ project team within 30 days.
- Final Submission – This phase includes explanations for the preliminary review queries. The final submission review comments are also given within 30 days by IGBC after which it awards the rating.
A project is required to satisfy all the mandatory requirements and minimum number of credit points in each section to achieve an IGBC Green Building Rating. The project team is required to make available all supporting documents at preliminary and final stages of submission for all the mandatory requirements and the credits attempted. Here is what needs to be submitted:
- General information documents – like project brief, project type, different types of spaces, occupancy schedule, number of floors and area statement.
- General drawings – this includes the master/site plan, floor plans, parking plans, elevations, sections, photographs and rendered images.
- Filled-in templates from the IGBC rating manual.
- Narratives and supporting documentation – like drawings, calculations, contract documents, declarations, purchase invoices and manufacturer cut-sheets/ letters/ material test reports for every mandatory requirement and for each credit bid.
-
Physical Audit
IGBC, carries out an exhaustive physical audit of the project through a third-party assessor team. This audit is done to ensure that the project meets all the demands for the rating. At this phase, IGBC counsellors recommend the project team on the possibility for further developments or improvements.
Physical audit is typically conducted when around 20-30% of the project work is complete. This offers an opportunity to the project team to take stock of the development made and look at the likelihood of integrating suggestions made by the audit team.
In addition to this, IGBC gathers energy and water performance related data annually from all the certified projects to confirm that they are able to achieve sustained performance as envisioned at the design stage.
- Final Award of Rating
After validating all the documents and submissions of the project team, IGBC rewards a final rating to the project. The different levels of ratings are as follows:
| Certification Level | Recognition |
| Certified | Good Practices |
| Silver | Best Practices |
| Gold | Outstanding Performance |
| Platinum | National Excellence |
| Super Platinum | Global Leadership |
The IGBC commemoration and certificate are normally provided to the project at the “Annual Green Building Congress”.
Final Thoughts
IGBC, is actively involved in promoting the green building movement in the country and hopes to rope in 10 billion sq ft by 2022. All the IGBC Green Building Rating Systems are well poised to develop world-class green building standards and practices, in fact, it wouldn’t be wrong to say that they are totally changing the shape of the Indian construction industry.
We hope, this all in one guide did help you understand everything about IGBC.
Read More: Go Green With LEED
Reference Links:
https://gbindia.wordpress.com/igbc-rating-system-2/
http://www.greenbusinesscentre.com/site/igbc/testigbc.jsp?desc=115754&event=115679
https://www.moneycontrol.com/news/business/personal-finance/-1844545.html
http://ishrae.in/newsdetails/The-IGBC-Green-Building-Certification-Process-/189
https://igbc.in/igbc/redirectHtml.htm?redVal=showgreenresSocietynosign#overview













