To experience the power of the sun, all you need to do is step outside on a cloudless summer day. Did you know, in just one hour the amount of energy the sun provides is enough to power our planet for one whole year? Yes, it’s true. Well, the use of solar power is not a new concept its been there from the ancient times, but the recent environmental concerns on the negative impact of burning the fossil fuels have made it one hot topic.
The unlimited energy that comes from the sun is free for use and environmentally friendly. Hence it sounds like one great solution to lower our dependence on the dirty and expensive fossil fuels. And this is simple, just discover practical and efficient ways to harness the energy from the sun.
The problem faced by most of the people when they decide to go solar is that they don’t understand where to begin from. If you are planning to harness the power of the sun – at your home or at a work building — here’s all that you need to know about solar energy systems, both active and passive.
Related: Solar Architecture – It’s Time To Design Buildings That Use Solar Energy Positively
How Does Solar Power Work, Anyway?
As of December 2016, India had a total installed large-scale solar capacity of 9,018 MW and a solar pipeline of 14,030 MW according to Mercom Capital Group. But how do these solar energy systems convert sunlight into electricity?
According to Live Science, a solar panel “works by allowing photons, or particles of light, to knock electrons free from atoms, generating a flow of electricity,”. Well, this is a technical explanation of saying that the photovoltaic cells of the solar panels convert the energy in sun’s photons to electricity.
Now don’t be worried about how this process works at night or on cloudy days. The solar panels store the surplus energy captured during the day to draw from it even when it’s night-time or a cloudy day.
Related: 12 Solar Energy Facts That Will Refute Your Misconceptions
What Are Active and Passive Solar Systems?
Modern solar energy systems harness the heat produced from the sun to power residential/industrial heating and cooling systems through the use of PV or photovoltaic panels. These are also called solar cells; such devices collect and convert solar energy into electrical energy. But how this energy is captured and distributed defines the real difference between the Active and Passive Solar Systems.
Flensburg 1. Active Solar Energy Systems
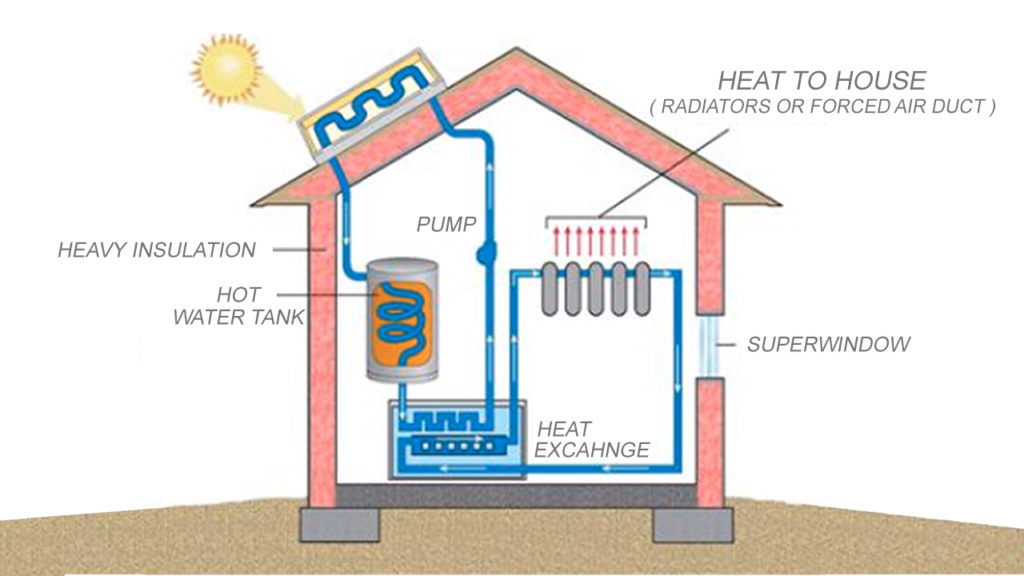
These systems use external sources of energy to power blowers, pumps and other types of equipment to capture, store, and convert solar energy. After solar energy is captured, it is stored for later used. Dependent on the intricacy of the design, these systems can heat/cool a home or even provide power to an entire building/neighbourhood. Typically, small systems are used to supply electricity for heating/cooling systems in homes and other buildings, and hi-tech large systems can supply power for entire communities.
| Egypt Pros | http://k9d.co.uk/wp-includes/block-patterns Cons |
| No need to worry about deriving power from sources other than the sun, this is because it utilizes the power of your external devices. It doesn’t release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.Heating of the PV panels helps keep them clean, even in bad weather conditions.No wind noise is generated from the solar panels. | Demands expensive external equipment.High maintenance cost for the equipment.The fluids which most efficiently store heat can pollute the air by releasing toxic chemicals into the air. |
The features of this system include:
- Solar collectors are made up of flat-plate PV panels, that are normally stationary and mounted. In hi-tech designs, these panels are commonly connected with each other to form modules. These solar collectors are more complex than passive systems in both design and mechanism.
- The solar collectors make use of liquid or air as conductors which store and convert energy. The ones which use liquid are called hydronic collectors, and the ones which contain air are known as air collectors.
- Liquid conductors are more popular than the ones which are air-based, this is because a liquid is normally more efficient at conducting heat.
The advanced design of these collectors makes an active solar system most cost-effective in terms of dipping reliance on traditional energy sources.
Saran 2. Passive Solar Energy Systems
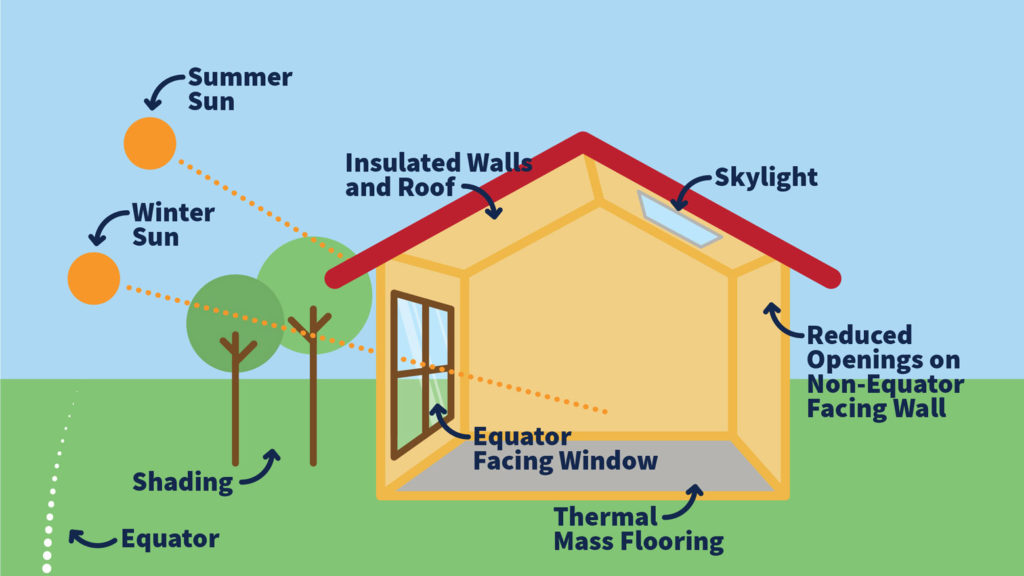
A passive solar system does not rely on external devices for operation. Simply put it doesn’t involve any mechanical devices or the use of conventional energy sources beyond what’s needed to regulate its control. Greenhouses, solariums, and sunrooms are classic examples of basic passive solar structures. Typically, the sun’s rays pass through the glass windows, which absorbs and retains the heat. The design and success of such systems depend totally on its orientation and the thermal mass of the structure’s exterior walls.
Investing in a passive solar system is a great idea when you are looking to power a small residence or office building.
| Pros | Cons |
| No external equipment needed, hence cheaper than active systems.It can bring down your energy expenditures by nearly 14 percent. A better option for health – because it doesn’t rely on radiators or furnaces which cause allergies or dry out your mucous membranes. | Its effectiveness depends on the weather.Not suitable for locations having warmer climates, as it can potentially overheat your buildings. Demands a cautious choice in windows for extreme success. |
The features of this system include:
- Typically, passive collectors rely on south-facing windows to capture solar energy.
- The design of the solar collectors in passive solar energy systems is based on the law of thermodynamics, that posits that heat transfers from warm to cool surfaces.
- The easiest method of transferring the heat from passive solar collectors is through convection.
The feat of the passive solar energy system is dependent on its orientation and the thermal mass of its walls, which governs its capability to absorb heat.
Which One Is Best For You?
Before getting into a debate it is first important to ask – Are ready for the switch to solar? Unquestionably, it’s a great way to contribute to a more sustainable environment, but before making the momentous decision, you will need to ensure its well calculated and researched.
We hope the information presented in this blog does help in you kick-start.
Curated by a building expert from Wienerberger India

You May Like: