Water is essential for human life, in fact, it can be considered fuel for humans. Even today, many think its supply is abundant, but to contradict that thought – Water Isn’t A Limitless Resource. More particularly the fresh potable water crucial for human survival is quickly depleting. Did you know? Global water usage continues to increase at 2X rate of population growth
But the question is – How Much Water Do We Have At Our Disposal?

You May Think – 70 percent of the earth is covered in water and take this fact for granted, but do you know how much of this is Fresh Water? The answer is – just 2 percent. What’s even more alarming is that out of that 2 percent, 1.6 percent is confined to the glaciers and polar ice caps. India holds the planets 2nd largest population at 1.3 billion which is expected to grow to 1.7 billion by 2050. It’s a daunting truth, but India finds itself unable to serve the massive populace with safe, clean water.
Unquestionably, the world is thirsty for water management and the key to achieve it is with active water efficiency and conservation practices in the buildings we live and in our daily lifestyles too.
What Is Water Efficiency?

We mentioned before, water is necessary for the sustenance of human life. Owing to the fact that this natural resource is rapidly exhausting, conservation is crucial. Now you may ask, is Water Conservation and Water Efficiency same? Well, although both the terms are often used synonymously, they differ in their actual meaning. Let’s understand them:
- Water Conservation – It implies curtailment of water usage and includes day-to-day demand management for better water usage.
- Water Efficiency – In simple terms, it means responsible use of fresh water and reducing the overall usage of water and minimizing wastewater. It also points toward using improved practices and technologies which deliver equal or better life service with reduced water consumption.
Water efficiency is a significant chunk of green buildings whose strategies and technologies lessen the amount of potable water consumed in buildings.
Water Efficiency In Green Buildings
 As access to fresh water continues to be a source of worry in many areas of the world (including India), water efficiency strategies in green building practices have become paramount to both new and existing construction efforts.
As access to fresh water continues to be a source of worry in many areas of the world (including India), water efficiency strategies in green building practices have become paramount to both new and existing construction efforts.
Green building mentions a building structure that is designed to be environmental-friendly and makes nominal and efficient use of natural resources. Such buildings are resource-efficient and eco-friendly during its entire lifespan starting from its construction to demolition. A Green building design largely emphasises on making effectual use of natural resources like water, energy, etc. while reducing several bad effects on the environment and the occupant’s health during its use. The 5 main gears of green buildings are:
- Site And Design Efficiency
- Reduced Energy Usage
- Reduced Water Consumption
- Environmentally Safe Construction Materials
- Better Air Quality
Considering water efficiency in Green Buildings, today several technologies are being used rainwater harvesting, recycling and reuse of grey water, low-flow fixtures, sensors etc. Water efficiency measures in residential and commercial buildings can greatly reduce water waste, yielding lower sewage volumes, reduced energy use, and bring in financial benefits too.
Green Building Rating Systems for Water Efficiency
Several rating systems for Green Building have been developed by various countries across the globe to rate the green buildings based on its degree of the environmental goals which have been achieved by them. In India, the main certifying agencies who consider water efficiency are:
- Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment (GRIHA)
GRIHA is our country’s own rating system which was jointly developed by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, Government of India and TERI. This rating system consists of 34 different categories under 4 main sections i.e. Site selection and site planning, Conservation and efficient utilization of resources, Building operation and maintenance, and Innovation.
- Indian Green Building Council (IGBC)
IGBC is the non-profit research institution formed by the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII). IGBC facilitates India’s green structures to become one of the green rated buildings.
- Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED, INDIA)
LEED, India Green Building Rating System is a standard point of reference both in India as well as worldwide for the design, construction and further, operation of high-performance green buildings. This is one of the main councils that provides green ratings to a building structure, whether an apartment, independent home or commercial property.
All the certifying agencies take into consideration how a Green Building performs on the scale for water efficiency and conservation.
Key Components Of Water Efficiency In Green Buildings
The three key components of water efficiency in green buildings according to the USGBC (U.S. Green Building Council) are:
- Reduce Indoor Potable Water Use
- Reducing Water Consumption to Save Energy
- Improve Environmental Well-Being
The strategies and technologies involved in a green building aim at reducing the amount of potable water consumed in buildings. Today there are several water conservation strategies which involve a low cost of implementation and have a very quick payback.
Water Efficient Technologies
Estimations vary, but every single person uses around 80-100 gallons of water each day. In addition to that, did you know the largest use of household water is to flush the toilet and post that in showers and baths? Here’s a rough breakup:

Alarming isn’t it? That’s exactly why Water Efficient technologies in buildings are imperative these days. With so much water getting wasted and overused, high volume of fresh water is getting drawn out resulting to depletion. Hence, water efficient technologies play a great role in conserving potable and non-potable water and eventually save the already scarce freshwater resources.
So, what does water efficient technologies include? Here is a quick rundown:
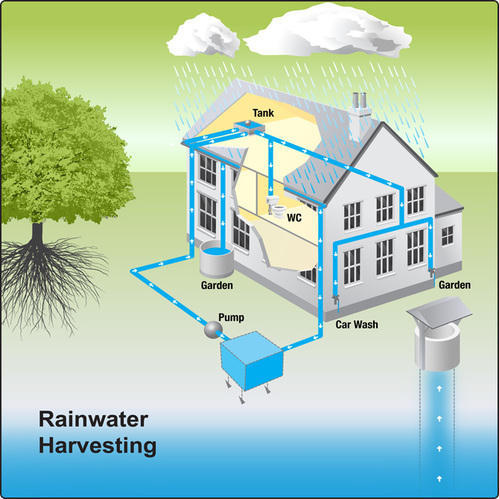
1. Rain Water Harvesting
We are sure you would have heard about this one as recently it has been grabbing a whole lot of attention. In simple terms, it is the active collection and distribution of rainwater which rather than going to the sewage is put into use in daily life. Typically, rainwater is collected from the rooftops, deposited in a reservoir with filtration. Once the water is purified, it is can be used for cultivation, gardening, and other domestic uses. One of the biggest uses of rainwater harvesting is in drier states where there is a lower rate of rainfall. They can store this water and can later purify it to make usable water or can use it for washing or watering plants.
Related: Rain Water Harvesting: Why, Benefits, Techniques & More
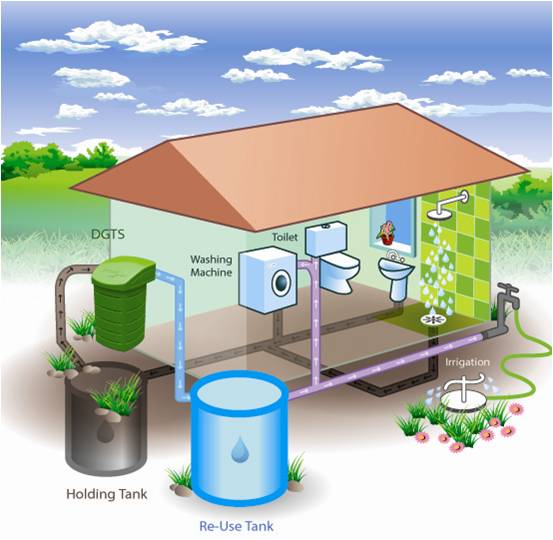
2. Grey Water Recycling
Grey water can be defined as untreated waste water which has not come into contact with water closet waste. Basically, it emanates from showers, bathtubs, bathroom wash basins, washing machines, and dishwashers. Treatment of greywater can include:
- Filtering
- Settlement of solids
- Flotation and separation of lighter solids
- Aerobic or anaerobic digestion
- Chemical or UV disinfection
But again, irrespective of the treatment such water is never safe to drink but can be used for flushing toilets, washing clothes and irrigation purposes. One of the major benefits of recycling greywater is that it is a huge source with a low concentration of organic matter.
Related: Grey Water Reuse: One Massive Step Towards Saving Water
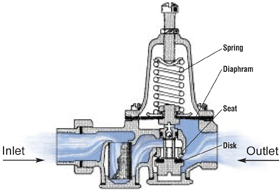
3. Pressure Reduction
These days, pressure reducing valves are being very commonly installed in high rise residential and commercial buildings to help to maintain a consistent water pressure at the water fixtures across the entire building from top to bottom. With these higher pressures, water flows through the system with greater flow through the terminal fixtures beyond rated flow capacities, this additional water is wasted and it serves no extra benefit to the rated performance. Most plumbing codes demand pressure reducing valves on the systems where water pressures exceed 80 psi and in most of the cases, pressures can be depressed through the implementation of supplementary pressure-reducing valves. In addition to that, higher pressures could break pipes and damage fixtures which could result in even greater water waste in domestic settings.
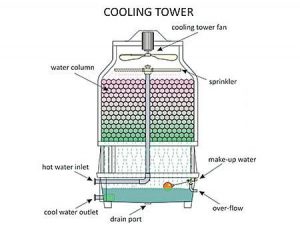
4. Cooling Towers
Green buildings make use of evaporative cooling systems to save on energy. Such systems use water for cooling. Keeping in mind the huge need to conserve water, the water used such cooling towers is non-potable water and the same is not drained out but recycled time and again and reused.
5. Low-Flow Plumbing Fixtures
Low-flow plumbing fixtures like faucets, shower heads, and toilets have become an increasingly common feature in green homes today, and for good reason. Large quantities of water are saved by the use of plumbing fixtures which are designed to operate with less water. For example, toilets were once made to function using 7 gallons per flush, but these days they can efficiently operate using only 1.3 gallons – this clearly means water savings of over 80 percent.
Related: How Water Efficient Toilets Can Save You Money & Help The Environment
Final Thoughts
The main objective of this blog was to stress on the need for water conservation of water and highlight the several technologies available for implementing water efficiency practices. Without our acknowledgment in the construction industry and in our everyday awareness, this crucial supply of water may be endangered. New technologies which use less water are becoming increasingly significant than ever before, this will ensure that we protect the existing sources of fresh water which is most essential for avoiding the crisis of water in the future.
Authored by a building expert from Wienerberger India
For any kind of assistance or tips on green building materials – drop us a word at gosmartbricks@gmail.com